On 14 November 2024, VinBrain introduced DrAid™ EndoAI, an advanced AI solution in gastrointestinal endoscopy, designed to assist doctors with real-time precision in detecting early signs of cancerous lesions. By enhancing accuracy during endoscopy process, DrAid™ EndoAI supports doctors in identifying abnormalities promptly, contributing to the early detection of gastrointestinal cancer and minimizing the risk of missing pre-cancerous signs.
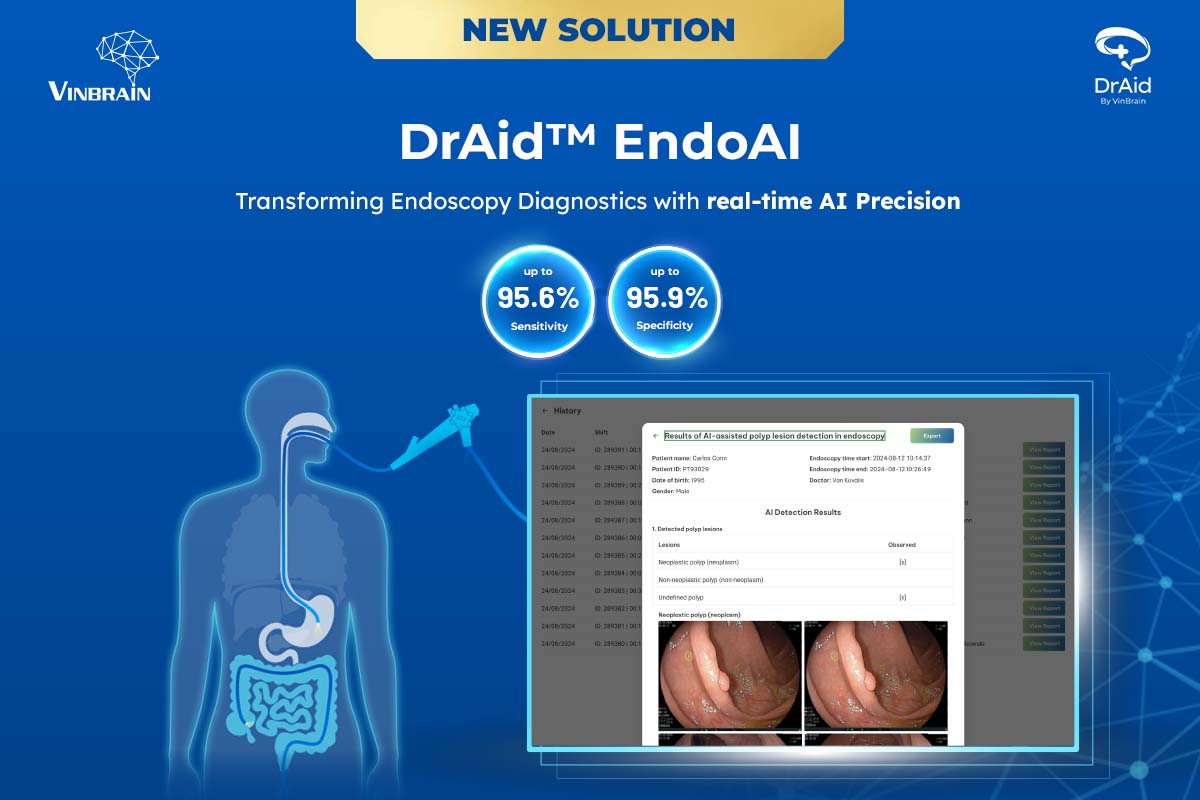
Trained on a big dataset of nearly 500,000 endoscopy images, DrAid™ EndoAI stands out with its ability to detect and classify up to 5 types of gastrointestinal lesions in real time. It also provides instant alerts for malignant findings, achieving a sensitivity of 95.6% and a specificity of 95.9%.
According to published data (*), the miss rate for upper gastrointestinal cancers, including esophageal and gastric cancer, through endoscopy is as high as 11.3%. Notably, for colorectal cancer, the miss rate for pre-cancerous lesions such as polyps or adenomas ranges from 20% to 47%. Additionally, the current number of endoscopists meets only 5-10% of actual demand. This creates immense pressure as doctors are required to perform endoscopies for a high volume of patients daily, increasing the likelihood of missing lesions during diagnosis.
DrAid™ EndoAI was developed to address these limitations. Unlike humans, AI is not affected by fatique and other subjective factors. AI technology in DrAid™ EndoAI provides entirely data-driven, objective assessments. By leveraging AI, endoscopists receive maximum support, gaining access to unbiased evaluations, reducing diagnostic errors and leading to more accurate outcomes for patients.
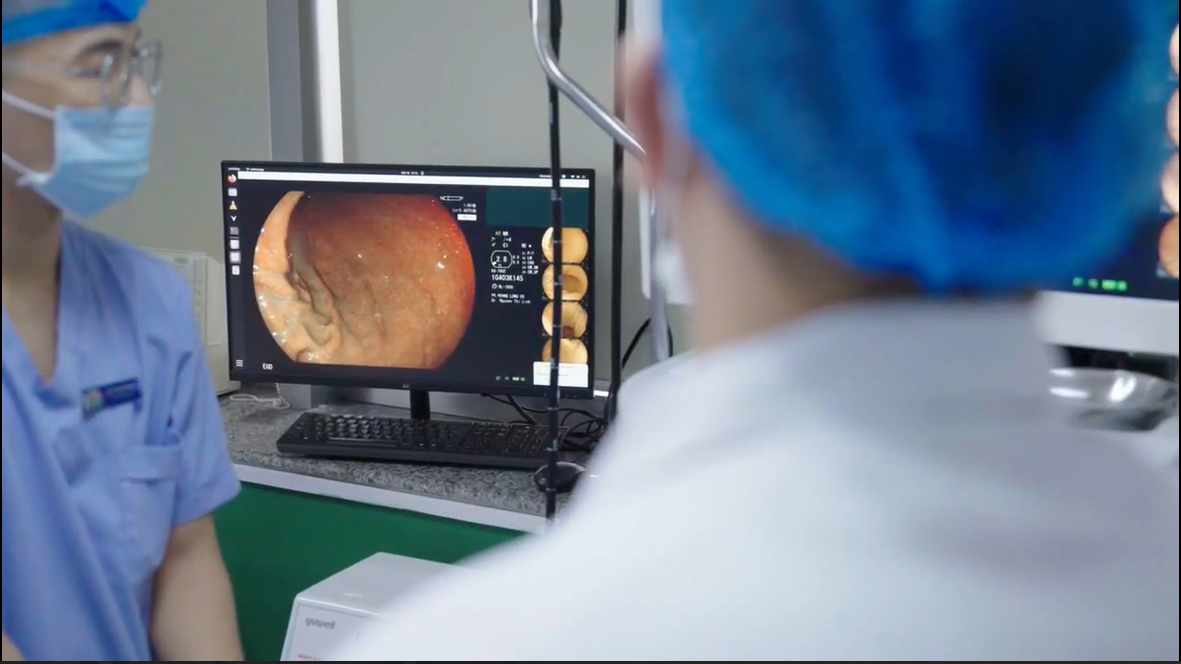
Developed in a short timeframe, DrAid™ EndoAI has gained a competitive edge over foreign solutions by leveraging VinBrain's technological capabilities and the deep knowledge of leading experts from the Institute of Gastroenterology and Hepatology. DrAid™ EndoAI provides a range of exceptional features that support efficient follow-up and the collection of valuable long-term data, including:
Prof. Dr. Dao Van Long, Former Director of Hanoi Medical University Hospital and Chairman of the Founding Council of Institute of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, shared about DrAid™ EndoAI after extensive testing: "We currently use eight AI software solutions in endoscopy - three from Vietnam, two from Japan, two from South Korea, and one from Hong Kong, allowing us to make comparisons. We have found that DrAid™ Endo is among the top three solutions we’ve used. There are several features we highly appreciate, such as automatic alerts with text on the screen and sound notifications for any suspicious malignant lesions, enabling doctors to quickly identify these critical findings quickly and efficiently".
Assoc. Prof. Dr. Nguyen Duy Thang, Chairman of Hanoi Society Gastroenterology shared: " I’ve got the opportunity to work with AI-integrated software in gastrointestinal endoscopy, specifically for the esophagus, stomach, and colorectal exams. AI delivers sharp, high-resolution images, enabling the detection of ultra-small lesions that are invisible to the naked eye. Additionally, AI helps save time and reduces the need for manpower in gastrointestinal endoscopy. Given these benefits, the widespread application of AI in gastrointestinal endoscopy is essential. This is also a growing trend globally and in Vietnam, in both healthcare and gastrointestinal endoscopy".
VinBrain showcased exceptional speed and dedication by bringing DrAid™ EndoAI from development to clinical testing at partner institutions - Hoang Long Clinics in just over two months. This is a significant achievement considering that AI products typically require 1-2 years to complete. According to VinBrain’s Founder and CEO, Mr. Steven Truong, this rapid advancement was driven by an urgent need for early cancer gastrointestinal detection, especially given the increasing rates of missing pre-cancerous lesions. “The VinBrain team is determined to launch a ‘Make-in-Vietnam’ AI-powered endoscopy solution in the shortest time possible to maintain our pioneer in healthcare AI in the Vietnamese market,” shared VinBrain CEO.
The launch of DrAid™ EndoAI solidifies VinBrain’s leadership in pioneering advanced AI solutions for healthcare. Expanding beyond AI platforms for radiology like X-rays, CT scans, and MRIs, this foray into endoscopy exemplifies the company’s technological prowess and unwavering commitment to tackling the toughest challenges in medicine. It is a bold step in VinBrain’s long-term strategy to build a comprehensive AI ecosystem for healthcare, driving innovations to save countless lives worldwide.
(*)
Pimenta-Melo, A.R., et al., Missing rate for gastric cancer during upper gastrointestinal endoscopy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2016. 28(9): p. 1041-9.
Zhao, S., et al., Magnitude, Risk Factors, and Factors Associated With Adenoma Miss Rate of Tandem Colonoscopy: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Gastroenterology, 2019. 156(6): p. 1661-1674 e11
Hằng, Đ.V., L.N. Hoa, and V.T. Hải, Đánh giá thực trạng và khảo sát nhu cầu xây dựng cơ sở dữ liệu hình ảnh, kết quả nội soi tiêu hóa tại các cơ sở y tế ở Việt Nam. Tạp chí Y học Thực Hành, 2020. 2(1126): p. 25-28
Top