
Artificial Intelligence (AI) in the medical field plays a crucial role in combating many severe diseases, such as liver cancer, breast cancer, and lung cancer. Cancer is a dangerous disease affecting multiple countries and ethnicities. As the second leading cause of death worldwide, cancer is extremely dangerous and often latent within the body, making early diagnosis very challenging. Therefore, the use of AI in early cancer detection is expected by scientists and medical professionals worldwide to address this revolutionary problem.

Artificial Intelligence (AI) has the potential to revolutionize cancer research, early diagnosis, and treatment through its powerful data analysis capabilities. Analyzing cancer-related big data opens opportunities for discoveries and complex medical research.
AI employs algorithms that mimic human brain functions to tackle highly complex problems healthcare providers encounter, such as abnormalities in human biological systems like cancer.
Experts predict that given the significant impact of AI and Machine Learning on daily life across various sectors, especially healthcare, these advanced technologies will have an even greater impact on the diagnosis and treatment of other diseases in the future.
One of the most notable advancements in the medical field in recent years is the application of AI in early cancer detection. According to surveys by leading experts, this is one of the most highly regarded AI applications in healthcare. Currently, many cancer cases are not diagnosed until the disease has progressed to the middle or late stages, making treatment more challenging and less successful. AI is the key to unlocking solutions to these unsolved problems.
In Vietnam, a Vingroup-funded enterprise called VinBrain has developed groundbreaking AI platforms serving over 2,000 doctors across more than 182 hospitals worldwide, aiding in treating over 2 million patients. One of their standout products is DrAid™ CT Liver Cancer, which has made a significant impression among medical professionals. This platform is one of the pioneering AI applications for early liver cancer detection globally. DrAid™ CT Liver Cancer is designed to assist radiologists by automatically detecting abnormal tumors in the liver through CT scans, providing clinical solutions for early diagnosis and classification of liver cancer, and aiding oncologists in developing more effective treatment plans.
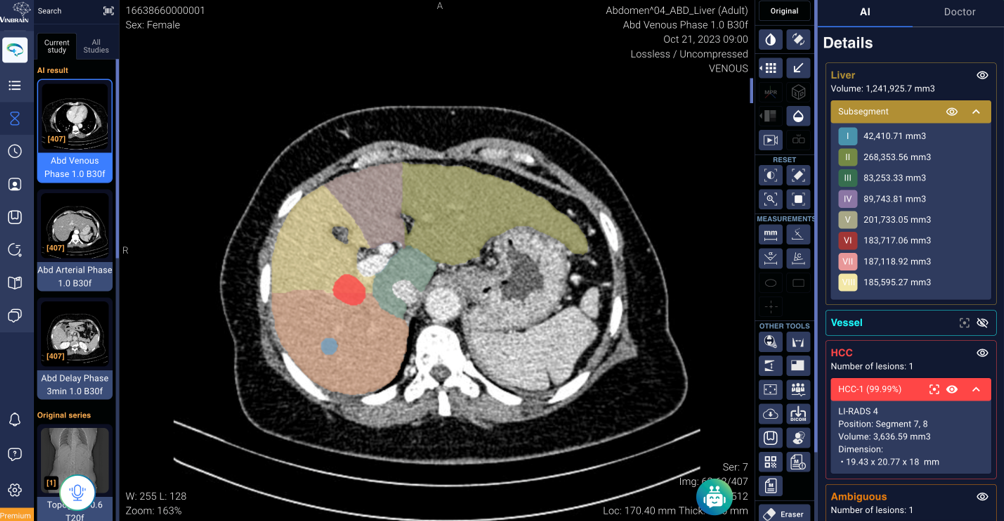
By integrating AI with advanced Multifaceted CT scan technology, DrAid™ CT Liver Cancer allows for imaging from multiple angles and depths, enabling the detection of small lesions as tiny as 5mm, often overdiagnosed by the human eye. The product includes four core features:
Lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer incidence and mortality worldwide. The 5-year survival rate for lung cancer patients is only 15.6%, and prognosis varies significantly across different clinical stages.
Professor Xu-Feng Huang from the University of Wollongong, Australia, has developed a new diagnostic method based on deep convolutional neural networks and extreme learning machines to classify benign and malignant nodules with an accuracy of 94.57% and an AUC (Area Under the Curve) of 0.95. Additionally, professors at Stanford University, USA, have created a solution named CheXNeXt to enhance the accuracy of lung cancer diagnosis from chest X-rays. Their findings indicate that the AI method achieves a sensitivity of 0.899, specificity of 0.901, and an AUC of 0.935 in diagnosing lung cancer within the community.
These results demonstrate that AI-based lung cancer screening can achieve high performance and help reduce radiologists' reading time. This provides doctors with additional diagnostic references, enhancing clinical treatment efficacy.
Current AI techniques offer quantitative analyses free from human subjectivity, aiding radiologists in detecting breast cancer at its earliest stages. Techniques such as image enhancement and denoising, which reduce background noise, can improve breast image quality, enabling radiologists to see anatomical structures that might not be visible to the naked eye.

Recently, researchers from the Breast Cancer Research Foundation (BCRF), Dr. Constance Lehman and Dr. Regina Barzilay, developed and tested a deep learning model based on mammography called MIRAI. To achieve this, they utilized a large patient dataset, analyzing and integrating risk factor information into the AI tool. The research team demonstrated that MIRAI can provide personalized, equitable, and cost-effective improvements in breast cancer risk prediction compared to traditional risk models. Notably, MIRAI delivers consistent results across different modalities, giving doctors greater confidence in its accuracy.
Colorectal cancer was the second leading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide in 2020. However, this disease can be completely cured if detected early. Colonoscopy is the gold standard for early colorectal cancer screening and detecting colorectal polyps. However, this method has limitations, including a high miss rate for small (<10 mm) or flat polyps that can be easily overdiagnosed.
With the support of AI technology in gastroenterology, AI software is now integrated into systems to assist doctors in diagnosing and improving the accuracy of automatic polyp detection and classification.
The leading roles of AI in early colorectal cancer diagnosis include Polyp Detection (CADe) and Polyp Characterization (CADx). CADe can reduce the miss rate of polyps, contributing to improved adenoma detection. At the same time, CADx can enhance the accuracy of optical diagnosis of colorectal polyps, facilitating the removal of non-cancerous lesions.
Although the applications above are just a few highlights of AI in healthcare, the medical community remains incredibly optimistic about AI's opportunities to doctors, patients, and healthcare facilities alike. Some of the notable opportunities include:
While the potential and opportunities of artificial intelligence in the medical field are undeniable, maximizing the benefits of this advanced technology presents numerous challenges for healthcare facilities and AI software and equipment companies.
In conclusion, cancer remains a global challenge that cannot be solved overnight. Although AI has achieved some initial successes, the challenges in data collection, processing, and analysis, which have led to the development of highly accurate methods, present a long journey ahead.
Nevertheless, with positive signals from AI developers in healthcare, we can look forward to a promising future where AI in early cancer diagnosis and even treatment becomes entirely feasible.
Source:
https://ezra.com/blog/ai-cancer-treatment
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC10047823/
Top